2'-O-4'-C-Locked-G(dmf) Phosphoramidite
2'-O-4'-C-Locked-G(dmf) Phosphoramidite - N (Normal) / 0.25g / 30mL screwed bottle-28 is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Shipping notes
Shipping notes
Details
Details
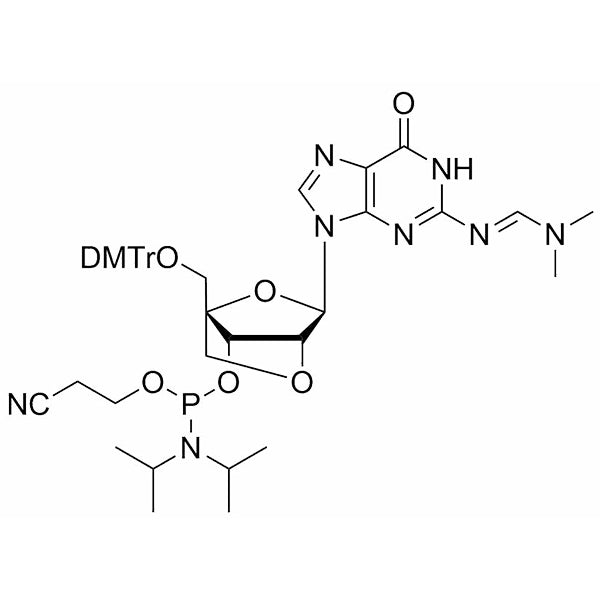
2’-O-4’-C-Locked-G(dmf) Phosphoramidite is a locked nucleic acid (LNA) phosphoramidite monomer for solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis.
It contains a bicyclic ribose in which a methylene bridge connects the 2’-oxygen (O) and 4’-carbon (C), locking the sugar in a C3’-endo conformation. It also contains a guanine (G) with dimethylformamidyl (dmf) base protection, a 5’-dimethoxytrityl (DMT) group for 5’-hydroxyl protection, and a cyanoethyl (CE) protecting group on phosphite.
LNA-modified oligonucleotides show enhanced binding strength, specificity, and nuclease resistance.
Applications
Detection & Diagnostics
LNA-modified oligonucleotides provide exceptional duplex stability, enabling highly sensitive detection such as hybridization probes and qPCR primers.[1][2]
Genotyping & Sequence Discrimination
The sharp mismatch recognition imparted by LNA enhances SNP genotyping and allele-specific PCR.[3][4]
Therapeutic Oligonucleotide Research
LNA modification is used to increase binding affinity and nuclease resistance of ASOs.[5][6]
Features
Other Notes
- Diluent: Anhydrous Acetonitrile.
- Storage: Store in a dry and inert atmosphere at -20 °C.
- Coupling: 6 minute coupling time recommended.
Reference
Specifications
Specifications
-
Catalog No.PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005
-
CAS No.709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2
-
SMILESO=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1
-
Molecular FormulaC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8P
-
Molecular Weight852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93
-
AppearanceOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matter
-
PurityHPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%
-
Storage Condition-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃
-
Moisture ContentK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/w
Documentation
Documentation
2’-O-4’-C-Locked-G(dmf) Phosphoramidite is a locked nucleic acid (LNA) phosphoramidite monomer for solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis.
It contains a bicyclic ribose in which a methylene bridge connects the 2’-oxygen (O) and 4’-carbon (C), locking the sugar in a C3’-endo conformation. It also contains a guanine (G) with dimethylformamidyl (dmf) base protection, a 5’-dimethoxytrityl (DMT) group for 5’-hydroxyl protection, and a cyanoethyl (CE) protecting group on phosphite.
LNA-modified oligonucleotides show enhanced binding strength, specificity, and nuclease resistance.
Applications
Detection & Diagnostics
LNA-modified oligonucleotides provide exceptional duplex stability, enabling highly sensitive detection such as hybridization probes and qPCR primers.[1][2]
Genotyping & Sequence Discrimination
The sharp mismatch recognition imparted by LNA enhances SNP genotyping and allele-specific PCR.[3][4]
Therapeutic Oligonucleotide Research
LNA modification is used to increase binding affinity and nuclease resistance of ASOs.[5][6]
Features
Other Notes
- Diluent: Anhydrous Acetonitrile.
- Storage: Store in a dry and inert atmosphere at -20 °C.
- Coupling: 6 minute coupling time recommended.
Reference
-
Catalog No.PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005PR2-005
-
CAS No.709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2709641-79-2
-
SMILESO=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1O=C1C(N=CN2[C@H]3[C@H](OC4)[C@H](OP(OCCC#N)N(C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@]4(COC(C5=CC=CC=C5)(C6=CC=C(OC)C=C6)C7=CC=C(OC)C=C7)O3)=C2N=C(/N=C/N(C)C)N1
-
Molecular FormulaC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8PC44H53N8O8P
-
Molecular Weight852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93852.93
-
AppearanceOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matterOff-white to yellow powder,free from visible foreign matter
-
PurityHPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%HPLC≥98.0%
-
Storage Condition-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃-20℃
-
Moisture ContentK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/wK.F.≤0.50% w/w
Why choose Hongene?
Trusted Partner in Nucleic Acid
Integrated Supply & Commercial Scale
With 26+ years of expertise, we control a secure supply chain for RNA raw materials and provide reliable GMP-grade oligo synthesis from research to commercial kilogram-scale production.
Proprietary Technology & IP
Our proprietary Chemoenzymatic Ligation Platform combines chemical andenzymatic methods, enabling high-putity, cost-effective, and large-scale production of RNA-based therapeutics.
Rigorous Quality
We implement multiple stringent QC steps, maintain ISO certifications, and ensure >99% batch-to-batch consistency, reducing scale-up and PPQ risks.
Manufacturing Scalability
Hongene operates 1.67 million sq. ft Oligonucleotide Manufacturing Facility, with advanced equipments including multiple OligoPilot™ and OligoProcess™ synthesizers (10-1800 mmol). 48 flexible production lines enable one-stop seamless scaling-up of API production from gram-level to tons and acheive high purity of 98%, meeting NMPA, FDA, and EMA standards.
Global Business Network
Our products and services reach over 40 countries and regions, supporting around 3,000 clients worldwide.